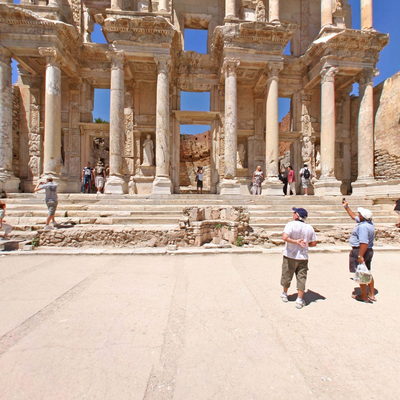
Ephesus - Roman Library of Celsus;
Ephesus (ɛfəsəs Greek: Ἔφεσος Ephesos; Turkish: Efes) was an ancient Greek city, built on site of the Arzawan capital, and later a major Roman city, on the coast of Ionia, near present-day Selçuk, İzmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era. In the Roman period Ephesus had a population of 33,600 to 56,000 people, making it the third largest city of Roman Asia Minor after Sardis and Alexandria Troas.
The city was famed for the Temple of Artemis (completed around 550 BC), one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. In 268 AD, the Temple was destroyed or damaged in a raid by the Goths. It may have been rebuilt or repaired but this is uncertain, as its later history is not clear. Emperor Constantine I rebuilt much of the city and erected new public baths. Following the Edict of Thessalonica from emperor Theodosius I, what remained of the temple was destroyed in 401 AD by a mob led by St. John Chrysostom. The town was partially destroyed by an earthquake in 614 AD. The city's importance as a commercial center declined as the harbor was slowly silted up by the Cayster River (Küçük Menderes).
Ephesus was one of the seven churches of Asia that are cited in the Book of Revelation. The Gospel of John may have been written here. The city was the site of several 5th-century Christian Councils, (see Council of Ephesus). It is also the site of a large gladiators' graveyard.
Today's archaeological site lies 3 kilometers southwest of the town of Selçuk, in the Selçuk district of İzmir Province, Turkey. The ruins of Ephesus are a favorite international and local tourist attraction, partly owing to their easy access from Adnan Menderes Airport.









Comments